在資料分析處理之前,一定要有好的資料。nltk之中建許多有語料庫,運用這些語料庫可大幅節省蒐集與整理文本資料的時間
nltk之中有許多內建的語料庫,可從nltk.cotpus選擇經分類的語料庫,對語料庫使用.fields()查看該語料庫的文本名稱
>>>nltk.corpus.gutenberg.fileids()
['austen-emma.txt',
'austen-persuasion.txt',
'austen-sense.txt',
'bible-kjv.txt',
'blake-poems.txt',
'bryant-stories.txt',
'burgess-busterbrown.txt',
'carroll-alice.txt',
'chesterton-ball.txt',
'chesterton-brown.txt',
'chesterton-thursday.txt',
'edgeworth-parents.txt',
'melville-moby_dick.txt',
'milton-paradise.txt',
'shakespeare-caesar.txt',
'shakespeare-hamlet.txt',
'shakespeare-macbeth.txt',
'whitman-leaves.txt']
>>>nltk.corpus.gutenberg.raw('austen-emma.txt')
"""
'[Emma by Jane Austen 1816]\n\nVOLUME I\n\nCHAPTER I\n\n\nEmma Woodhouse,
...
"""
>>>nltk.corpus.gutenberg.sents('austen-emma.txt')
[['[', 'Emma', 'by', 'Jane', 'Austen', '1816', ']'], ['VOLUME', 'I'], ...]
nltk.corpus.gutenberg.words('austen-emma.txt')
['[', 'Emma', 'by', 'Jane', 'Austen', '1816', ']', ...]
布朗語料庫是第一個百萬詞級的英語電子語料庫的,由布朗大學於1961 年創建。這個語料庫包含500 個不同來源的文本,按照文體分類,如:新聞、社論等
>>> from nltk.corpus import brown
>>> brown.categories()
['adventure', 'belles_lettres', 'editorial', 'fiction', 'government', 'hobbies',
'humor', 'learned', 'lore', 'mystery', 'news', 'religion', 'reviews', 'romance',
'science_fiction']
布朗語料庫是一個研究文體之間的系統性差異——一種叫做文體學的語言學研究——很方便的資源。讓我們來比較不同文體中的情態動詞的用法。第一步是產生特定文體的計數。
from nltk.corpus import brown
>>> news_text = brown.words(categories='news')
>>> fdist = nltk.FreqDist(w.lower() for w in news_text)
>>> modals = ['can', 'could', 'may', 'might', 'must', 'will']
>>> for m in modals:
... print(m + ':', fdist[m], end=' ')
can: 94 could: 87 may: 93 might: 38 must: 53 will: 389
當語料文本被分為幾類,如文體、主題、作者等時,我們可以計算每個類別獨立的頻率分佈。這將允許我們研究類別之間的系統性差異。
將布朗語料庫中的每份文本,依照類別作出配對
>>>genre_word = [(genre, word)
... for genre in [ 'news' , 'romance' ]
... for word in brown.words(categories=genre)]
>>>genre_word[:3]
[('news', 'The'), ('news', 'Fulton'), ('news', 'County')]
>>>genre_word[-3:]
[('romance', 'not'), ('romance', "''"), ('romance', '.')]
再把genre_word丟進ConditionFreqDist裡,就可以在cfd中依照類別找出單字頻率
>>> cfd = nltk.ConditionalFreqDist(genre_word)
>>>cfd['news'].most_common(10)
[('the', 5580),
(',', 5188),
('.', 4030),
('of', 2849),
('and', 2146),
('to', 2116),
('a', 1993),
('in', 1893),
('for', 943),
('The', 806)]
詞彙語料庫是Unix中的/usr/share/dict/words文件,被一些拼寫檢查程序使用。我們可以用它來尋找文本語料中不尋常的或拼寫錯誤的詞彙
def unusual_words (text):
text_vocab = set(w.lower() for w in text if w.isalpha())
english_vocab = set(w.lower() for w in nltk.corpus.words.words())
unusual = text_vocab - english_vocab
return sorted(unusual)
>>> unusual_words(nltk.corpus.gutenberg.words( 'austen-sense.txt' ))
還有一個停用詞語料庫,就是那些高頻詞彙,如the,to和also,我們有時在進一步的處理之前想要將它們從文檔中過濾。停用詞通常幾乎沒有什麼詞彙內容,而它們的出現會使區分文本變困難。
```python
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stopwords.words( 'english' )
定義一個函數來計算文本中沒有在停用詞列表中的詞的比例:
>>> def content_fraction (text):
... stopwords = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words( 'english' )
... content = [w for w in text if w.lower() not in stopwords]
... return len(content) / len(text)
...
>>> content_fraction(nltk.corpus.reuters.words())
0.7364374824583169
>>>phrase = ['yee','poi','qaz']
>>>print(phrase*2)
>>>print(phrase+['eee'])
>>>print(phrase[2])
>>>print(phrase[1:3])
>>>print(sorted(phrase))
['yee', 'poi', 'qaz', 'yee', 'poi', 'qaz']
['yee', 'poi', 'qaz', 'eee']
qaz
['poi', 'qaz']
['poi', 'qaz', 'yee']
>>>persuasion = nltk.corpus.gutenberg.words( 'austen-persuasion.txt' )
>>>print(len(persuasion))
>>>print(len(set(persuasion)))
98171
6132
nltk.corpus.brown.raw(categories='humor')
nltk.corpus.brown.raw(categories='news')
from nltk.corpus import state_union
>>> cfd = nltk.ConditionalFreqDist(
(target, fileid[:4])
for fileid in state_union.fileids()
for w in state_union.words (fileid)
for target in [ 'men' , 'women','people' ]
if w.lower().startswith(target))
>>>print(cfd['men'].items())
>>>cfd.plot()
dict_items([('1945', 2), ('1946', 16), ('1947', 8), ('1948', 5), ('1949', 2), ('1950', 6), ('1951', 9), ('1953', 5)...]

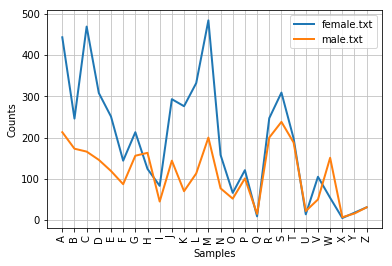
>>> names = nltk.corpus.names
>>> cfd = nltk.ConditionalFreqDist(
... (fileid, name[0])
... for fileid in names.fileids()
... for name in names.words(fileid))
>>> cfd. plot()
>>>def word_freq(cate,word):
... return nltk.FreqDist(nltk.corpus.brown.words(categories=cate))[word]
>>>word_freq('lore','cry')
9
參考資料:Python 自然語言處理第二版 https://usyiyi.github.io/nlp-py-2e-zh/2.html
